在这个示例中,我们将引入一个新的量子操作——受控门,它也是量子计算中最常用的操作之一。
In this example, we introduce a new quantum operation, the controlled gate, which is also one of the most frequently used operations in quantum computing.
示例五、受控非门
Example 5. Controlled not gate
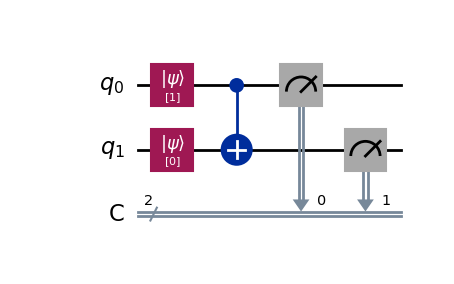
在这个量子电路中,我们创建了 q0 和 q1 两个量子位元,一开始我们分别把它们初始化为 1 和 0。
In this quantum circuit, we have two qubits, q0 and q1, which are initialized to 1 and 0 respectively.
然后,我们对它们使用了一个 受控非门,受控非门 会根据 控制位元 q0 来决定是否对 目标位元 q1 进行取反操作,如果 控制位元 q0 的值为 1 则将对 目标位元 q1 进行取反操作,反之则不进行取反操作。
We then apply a Controlled-NOT gate which flips the target qubit q1 if the control qubit q0 is 1, and does nothing otherwise.
最后我们再测量这两个量子位元,并将测量结果保存到 经典位元 c0 和 c1 中。
Finally, we measure both qubits, storing the results in classical bits c0 and c1.
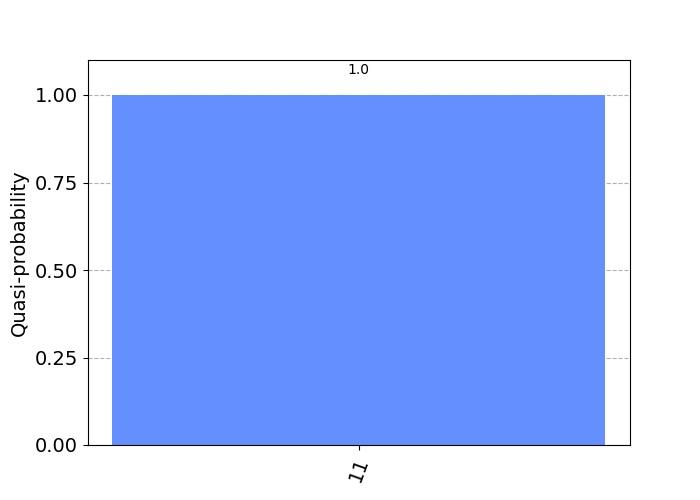
经过对该量子电路的采样测量,我们将以 100% 的机率得到二进制数值 1 1。这是因为 受控非门 的 控制位元 q0 等于 1,所以会 受控非门 对 目标位元 q1 进行反转,将其从 0 反转为 1。
By sampling the measurement of the quantum circuit, we will get binary value 1 1 with 100% possibility. This is because the control qubit q0 of the Controlled-NOT gate is 1, so the Controlled-NOT gate will flip the target qubit q1, turning it over from 0 to 1.