之前的两个示例都是在单量子位上进行的操作,接下来的这个示例将是一个关于双量子位电路的示例。
The previous two examples were operations on a single qubit, the upcoming example is an example of a circuit with two qubits.
示例三、双量子位的操作
Example 3. Two-Qubit Operation
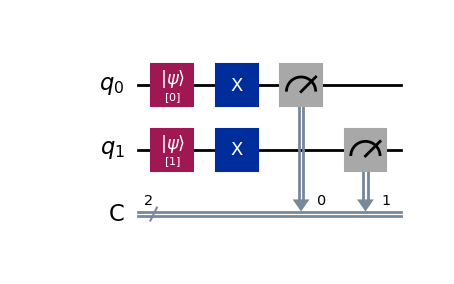
我们定义了 q0 和 q1 两个量子位,分别初始化 q0 为 0;初始化 q1 为 1。接下来我们使用泡利 X 门分别对这两个量子位进行反转,最后我们对反转后的量子为进行测量。
We define two qubits q0 and q1, initialize q0 to 0; initialize q1 to 1. Next, we use the Pauli X gate to flip the two qubits respectively, and finally we measure the flipped qubits.
需要注意的是:我们将量子位 q0 的测量结果保存到了经典位中的 c0 位,将量子位 q1 的测量结果保存到了经典位中的 c1 位。
Note that: we save the measurement result of qubit q0 to the classical bit c0, and the measurement result of qubit q1 to the classical bit c1.
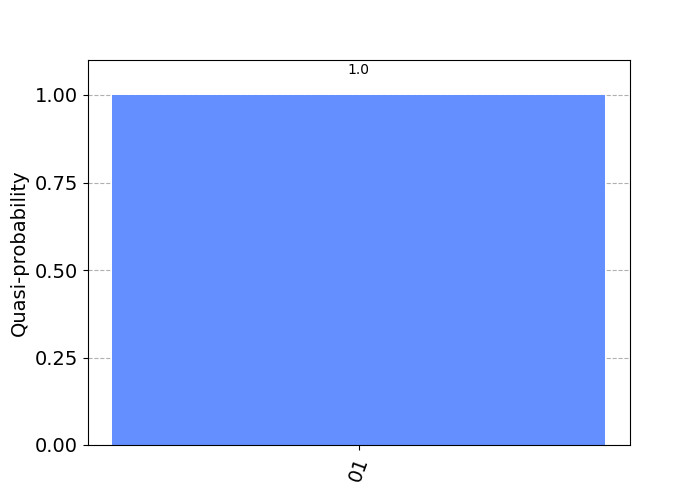
通过对这个量子电路的采样测量,我们将有 100% 的机率取得二进制数值 0 1。因为虽然我们将 q0 与 q1 分别初始化为 0 与 1,但是在之后我们对它们分别使用泡利 X 门进行了反转。
By sampling the measurement of this quantum circuit, we will have a 100% probability of getting binary value 0 1. Because although we initialize q0 and q1 to 0 and 1 respectively, we then use Pauli X gates to flip them respectively.