我们将使用四个基础示例对量子电路的大致形式和运行规则进行说明,本示例为其中的第二个示例。在这个示例中,我们会看到量子门是如何在量子电路中发挥作用的。
We will use four basic examples to explain the general form and operation rules of quantum circuits, and this is the second example. In this example, we will see how gates work in a quantum circuit.
示例二、量子门的使用
Example 2. Using Quantum Gates
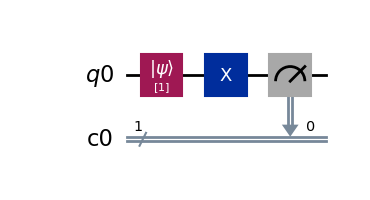
对比之前“示例一”中的量子电路,我们看到这个新的量子电路中出现了一个写着字母 X 的方框,字母 X 表明了这是一个 X 门,或者我们可以称它为 泡利-X 门。
In contrast to the Quantum Circuit in “Example 1” above, we see a box with the letter “X” in it in this new Quantum Circuit, the letter “X” implies a “X Gate” or we can call it “Pauli-X Gate”.
该量子门会对量子位的 0 与 1 进行反转,例如:将量子态 0 转换为量子态 1;或者将量子态 1 转换为量子态 0 。这个性质类似经典电路中的 非门,我们也可以称它为量子电路中的 非门。
This Quantum Gate flips a Qubit’s state from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0. This property is similar to the NOT Gate in a classical circuit, so we can call it the NOT Gate in Quantum Circuit as well.

通过采样测量,我们会有100%的机率得到数值 0 ,这是因为我们虽然一开始初始化量子位 q0 为 1,但是之后我们又使用 X 门对它进行了反转。
Through the measurement by sampling, we have a 100% probability to get value 0 , that is because although we initialized the qubit q0 to 1, we used an X gate on it to reverse it later.